TERRITORY/MOBILITY
Mobility is a fundamental need and its planning influences infrastructural and spatial but also social structures. The research projects that deal with this focus not only seek to develop a better understanding of the role and function of mobility, but also focus on the interrelation between mobility and space. Spatial and strategic concepts are designed to contribute to the promotion of active and emission-free forms of mobility and to increase the quality of public space, as well as to enable fair access to mobility.
KombiMO II – Combined mobility in Graz
Multimodal nodes as urbane mobility solution, phase II
07/2015 - 06/2018

© KombiMo-Researchteam
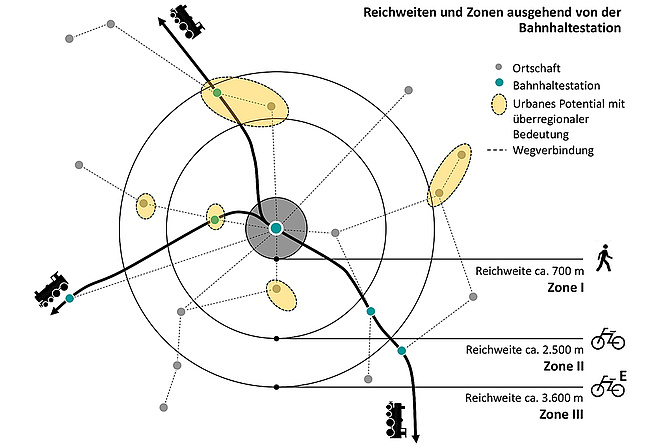
An important future challenge will be to meet the mobility needs of the Graz population by offering services that are as environmentally friendly, resource-saving, affordable, socially acceptable and attractive as possible. The mobility strategy of the City of Graz decided by the Municipal Council of the City of Graz provides for qualitative measures to shift the "modal split" in the direction of public transport and to push for new forms of mobility that support it. As part of the KombiMo II demonstration project, five multimodal nodes will be established as mobility hotspots for linking public transport, cycling, car sharing with e-vehicles and e-taxis and made accessible via a multimodal map. In the future, Graz residents will be able to meet their mobility needs comprehensively without having to own their own car. When placing the multimodal nodes, attention was paid to a good distribution among the user groups and the urban area as well as the inclusion of the two large urban development projects "Smart City Waagner Biro" and "Reininghaus". As part of the demonstration project, multimodal nodes will be implemented at the following locations: Hasnerplatz, Schillerplatz, Messe, Smart City (List-Halle), Reininghaus (Central Park). In the course of the project, the framework conditions for the transfer to regular operation and, if necessary, a step-by-step rollout are to be verified.
Projekt managment:
- Holding Graz Linien
Projekt partner:
- City Graz, Department of Traffic Planning
- Energie Graz GmbH
- WKO Steiermark – Fachgruppe für Personenbeförderung mit PKW
- e-mobility Graz GmbH
- PLANUM FH Joanneum Quintessenz
- Institute for Road and Traffic Engineering
- Institute of Urbanism
- Institute of Automotive Engineering
Sponsor:
- BMVIT – e-Mobilität for all: Urban electric mobility
ERP_hoch3
Energy Spatial Planning for Smart City Quarters
and Smart City Regions
09/2014 - 08/2016

© Michael Malderle, Institute of Urbanism
As part of the nationally funded research project "ERP_hoch3", the topic of energy space planning was examined, examined and simulated on three focal planes. While "ERP" stands for energy planning, the "3" stands for three different spatial references: urban quarters, public transport axes and intercommunal area potentials of renewable energies (region).In three Austrian city regions (Vienna, Graz, Feldkirch-Vorderland), existing control instruments with energy relevance were researched and from this, actionable recommendations for energy area planning were developed for city regions. The end product consists of three guidelines for urban planning, neighborhoods along public transport stops (public transport axes) and intercommunal land potentials for renewable energy sources.The research area in Vienna is located around the two largest inner-city development areas, the Northwest and North Railway Station. The study area in Graz coincides with the peripheral area of the Smart City target area Graz-Süd. Two railway axes were investigated, which proceed from the defined potential zones in Vienna and Graz: "Wien - Gänserndorf" (Northern Railway) and "Graz - Gleisdorf" (Eastern Railway).
Project Lead:
Institute of Spatial Planning, Department Regional Planning and Regional Development, TU Vienna
Project Partner:
- Institute of Urban Design, Graz University of Technology
- Institute of Process and Particle Technology, Graz University of Technology
Grantor:
- BMVIT - city of the future