Project Objectives
The need for deeper expertise in sustainable chip design, manufacturing and green applications goes hand in hand with the ideals of the next generation students to contribute to a sustainable environment. Meaningful work for a green and circular economy will be an important argument to attract future engineering talents, and students will have the chance to act as change agents for a sustainable, green, liveable future that harnesses the possibilities of technology without destroying the environment.
The GreenChips-EDU project plans the following activities:
Objective 1: Addressing skills needs.
The project aims to address skills needs in the microelectronics industry, particularly focusing on green chips and applications. The initiative involves collaboration among fifteen partners from seven European countries, integrating education, research, and businesses. With a vision to empower individuals through university education and lifelong learning, the project targets crucial issues in society, such as the transition to green energies. It emphasizes the importance of efficient power electronics, addressing energy consumption in cloud data centers, and promoting the design of environmentally friendly microelectronics.
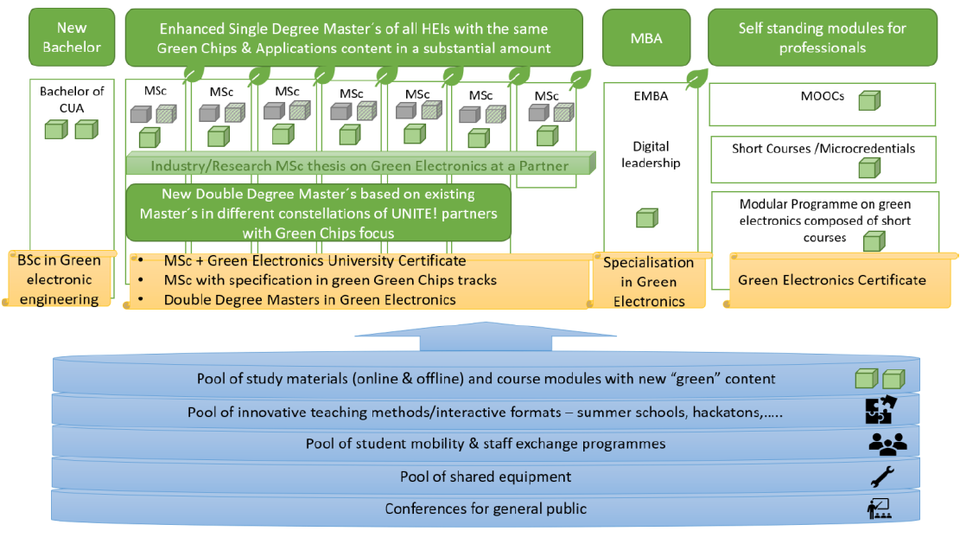
GreenChips-EDU offers a range of degree programs and modules, including a new bachelor’s program in green electronics and enhancements to existing master’s programs. The efforts include redesigning curricula, engaging with business partners, incorporating a holistic view of microelectronics, and developing collaborative learning materials. The project also focuses on online courses, interactive formats, and community-building activities.
Additionally, the consortium plans to establish an innovative bachelor program at the Carinthia University of Applied Sciences to address the demand for skills in green electronics. The project extends to the development of an MBA program and self-standing modules for upskilling and reskilling, emphasizing a sustainable and circular economy mindset in the microelectronics industry. The target audience includes management-level students, ICT specialists, and individuals from non-ICT backgrounds, with a special focus on the energy sector workforce involved in renewables deployment.
Objective 2: Attracting qualified teaching staff and students
As there are currently many industry sectors competing for talents, the provision of excellent training possibilities does not necessarily ensure a skilled workforce and teaching staff as needed to fulfil the goals of the European Chips Act. GreenChips-EDU will implement the following activities:
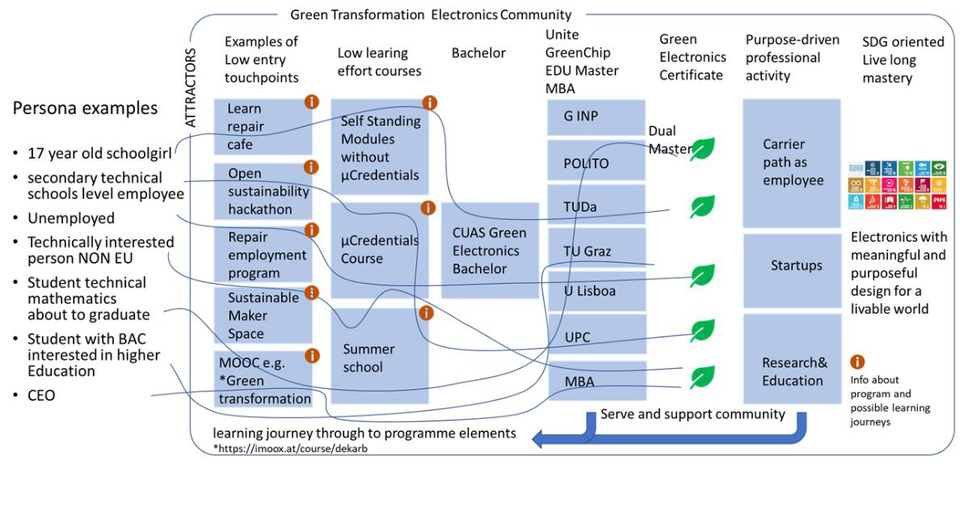
Attracting staff – The competences of the consortium partners including the associate partners will enable an extensive staff exchange programme between the universities and also provide know-how to the students via external lecturers from businesses and research. They will not only be involved in theory lectures but also participate in the interactive formats as summer schools.
Staff exchanges also can take place virtually: by proper synergy and harmonization of digitalized courses, the students will have access not only to the staff of their local university, but also to the staff of the other partners. For selected and specific topics that require hands-on activity and/or physical interaction with the teaching staff, traditional staff exchanges and/or student mobility will be implemented.
Attract and support students – Student mobility will be fostered in addition to already existing programmes within Erasmus and the Unite! Partnership. Internships, summer schools or hackathons will be organized at different locations of the partners within Europe. Setting up double degree programmes will also enhance student mobility. Via scholarships, either as local programmes, co-financed by industry partners, or in form of mobility scholarships, financial support can be provided for students. The criteria for the awarding of scholarships will have a clear focus on diversity, equity and inclusion.
Objective 3: Upgrading digital solutions, equipment and infrastructure.
The microelectronics education to be successful requires the students to (a) use up-to-date design infrastructure, (b) have access to fabrication facilities, and (c) do lab testing of fabricated chips. GreenChips-EDU provides the opportunity to join forces and create synergy to reduce costs and remove barriers. For (a) a cloud CAD infrastructure will be created, either fully shared among partners or partially replicated, with common hardware (i.e., rack servers with same characteristics), same software structure (OS, CAD tools, shared licenses, remote access mechanisms). For (b), three target technologies will be selected (i.e., one for power electronics, one for analog and mixed-signal microelectronics, one for purely digital microelectronics) and fabrication costs shared via multi-project mechanisms (see for example what Google is doing with the Skywater technology). For (c) a common testing platform will be shared (e.g., shared Printed Circuit Board (PCB) for chip testing, share access to testing equipment with a mechanism of credits for access to allow students to access tools that otherwise they would never use).
Objective 4: Establishing structural and sustainable partnerships.

The Unite! Consortium provides a broad network of public and private connections and links to the administration of 9 different European countries. It sets a new model for a European virtual and physical inter-university campus. This extensive network can be leveraged to create new opportunities for teaching as well as to identify new ways to deliver education and training. For example, the consortium can benefit from the development of open batch systems and the exploration of microcredentials systems, which can be used to deliver training more efficiently. The JPROVirtual project10 is another excellent example of the cooperation that can be achieved .It aims to build double degrees with a virtual component, which can be assumed by some of the trainings delivered in this project. This approach allows students to acquire knowledge and skills that and provides them with a competitive advantage in the job market. Unite! and GreenChips-EDU will transform European higher education in microelectronics through multidisciplinary, multicultural and multilingual education, research and entrepreneurship.
GreenChips-EDU will create a sustainable network of research, HEIs and industrial infrastructures, also linking HEIs with stakeholders in their regional context. As described in 3.1 and underlined with the KPIs related to R&D cooperations, external lectures industry collaborations and shared equipment, the consortium partners will lay the fundament for deepening these joint activities and enlarge the network also with the help of associated partners and cluster organizations.

